By the end of June 2025, the cumulative newly installed Photovoltaics (PV) grid-connected capacity in the first half of the year had reached 211.61 GW. Among this, distributed PV installations accounted for 112.81GW, while centralized PV installations totaled 98.80GW. Photovoltaics have thus become the fourth principal source of electricity in China, following thermal power, hydropower, and wind power.
Within the PV inverter market, string inverters and centralized inverters remain the dominant technologies. In 2024, string inverters captured 80% of the market share, whereas centralized inverters accounted for 20%. Since 2017, when the market share of string inverters first surpassed that of centralized systems, their advantage has continued to expand, resulting in a clear dominance. Projections suggest that this market structure will remain essentially stable in 2025 and in the foreseeable future, indicating that string inverters will continue to play the leading role in the coming years.
However, as the scale of the PV market continues to expand, the rapid influx of new entrants has intensified competition across the industry. This development has driven technological iteration into a phase of heightened intensity, accompanied by persistent price erosion, shortened innovation cycles, and accelerated progression toward solutions with higher efficiency and lower costs. A salient trend has become evident: compared with the field of energy storage power conversion systems (PCS), string inverters have demonstrated more extensive application of power modules, with the development and deployment of high-power models proceeding at a faster pace. It is expected that by late 2025 or early 2026, string inverters with power ratings exceeding 400 kW will be mass-produced. In parallel, the forthcoming release of the national standard for 2 kV DC bus systems (NB/T 32004-202X) will provide guidance and normative support for the adoption of new technologies. Moreover, the rated power of single-unit string inverters is approaching that of single-module centralized inverters. This shift enhances application flexibility, enabling modular combinations to address a wider spectrum of end-user power demands.
In response to intensified competition across multiple dimensions—cost, product models, and technology—solutions that reduce development complexity have become increasingly valuable. To this end, Firstack offers a series of standardized IGBT driver solutions, designed to assist PV inverter manufacturers in achieving more efficient, streamlined, and less resource-intensive product development. These solutions provide a unique position of comparative ease within an otherwise highly competitive landscape.
1. 2FSC0110 Series Driver Core
- Product Positioning: A protection-free IGBT driver core unit specifically designed for small to medium-power inverters.
- Topology Compatibility: Supports various topologies, including two-level, T-type three-level, and NPC-I three-level configurations.
Drive Performance: Delivers a continuous output power of 1W or 2W per channel (varies by model) under an ambient temperature of 85°C.

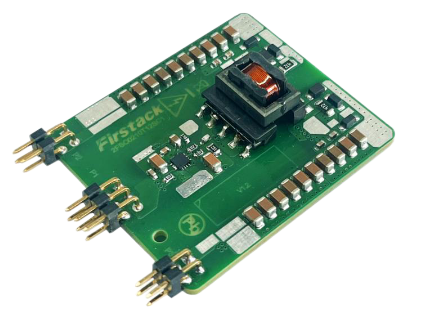
2. 4FSC0110T12A1 (Four-Channel Integrated Type)
- Iterative Upgrade: Optimized based on the 2FSC0110 architecture.
- Structural Innovation: Utilizes planar transformer technology to achieve a compact design with a maximum thickness of ≤6.3mm.
- Performance Enhancement: Delivers a maximum output power of 1.2W@10A.
- Application Expansion: Compatible with NPC-I/ANPC three-level topology systems.
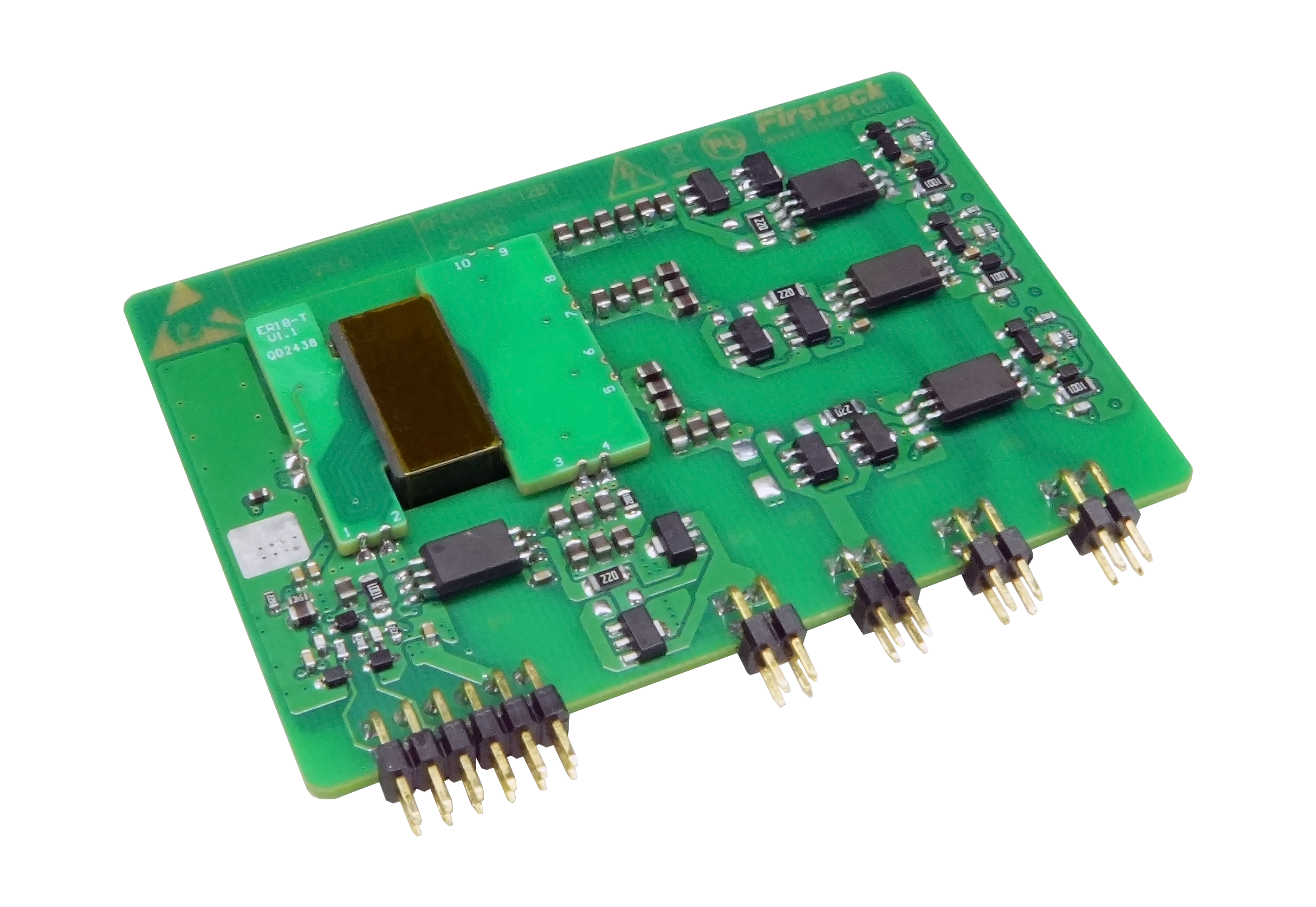
3.6FSC0110T12 Series (Six-Channel Integrated Driver)
- Power Supply Optimization: Adopts a dual-stage voltage stabilization architecture to ensure highly stable output voltage.
- Enhanced Control Functionality: Features an added power enable (EN) pin, supporting system-level soft-start functionality.
- Model Variations:
- C1: Designed for IGBTs, providing gate drive voltages of +15V (turn-on) and -6V (turn-off).
- C2: Optimized for SiC MOSFETs, delivering gate drive voltages of +18V (turn-on) and -3V (turn-off).
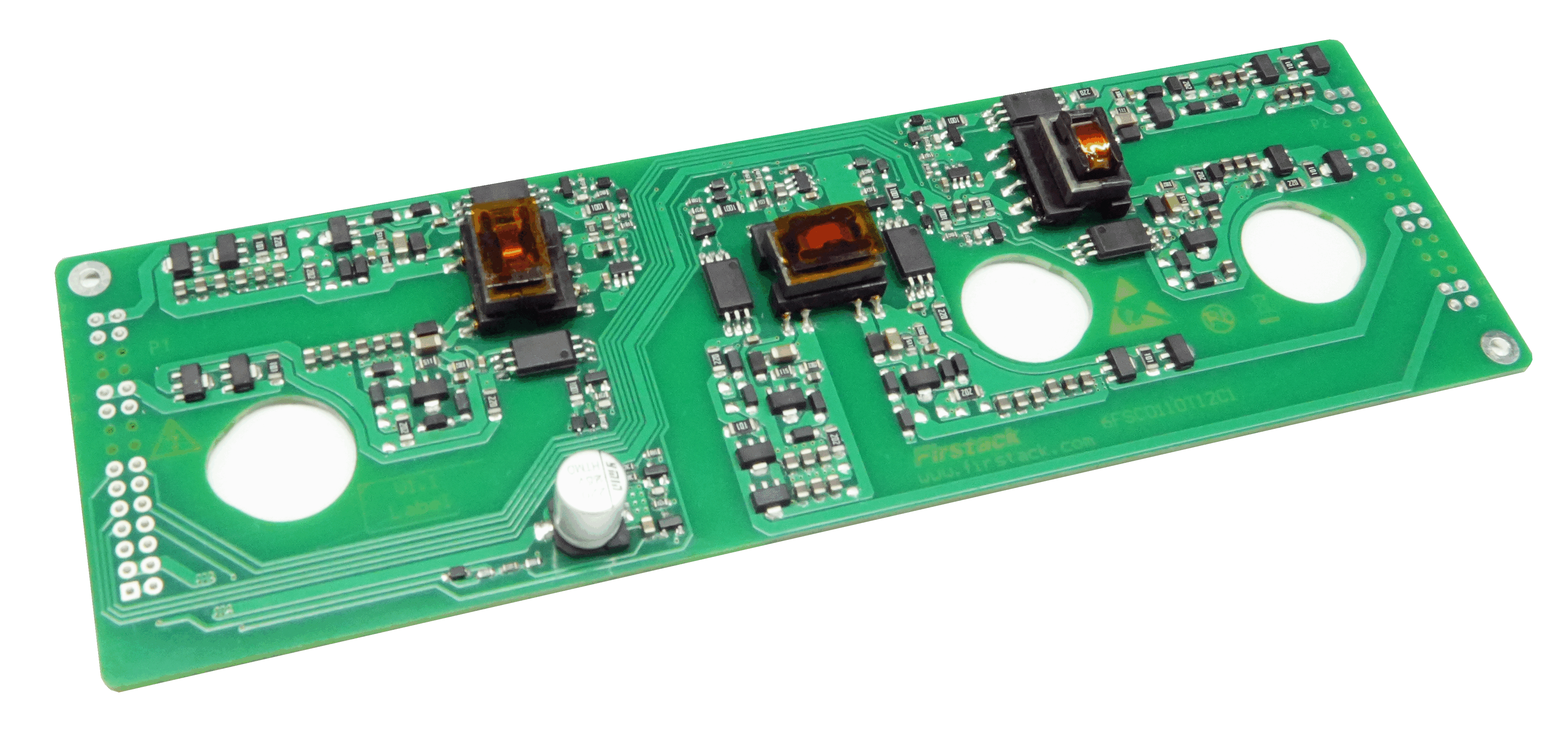
Product Test Data
Model Number: 2FSC0210TSC1
| Parameter | Min. | Typ. | Max. |
| Supply Voltage/V | 12 | ||
| Output Power per Channel (85°C)/W | 2 | ||
| Gate Peak Current/A | -10 | +10 | |
| Withstand Voltage Test/Vac | 5000 | ||
| Operating Temperature/°C | -40 | 85 |
Test Waveforms
Power Supply Ripple:
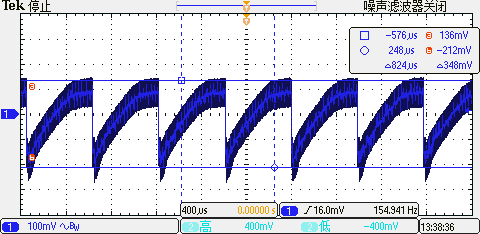
TOP Full Load, Positive Rail Ripple: 348 mV
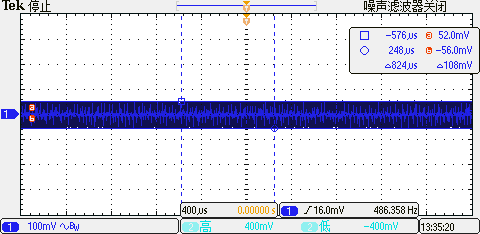
TOP No Load, Positive Rail Ripple: 108 mV
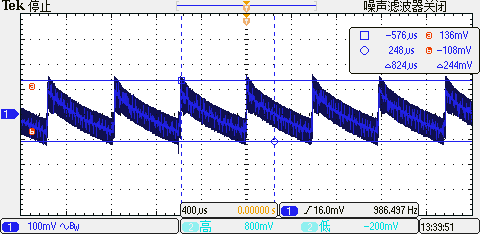
TOP Full Load, Negative Rail Ripple: 244 mV
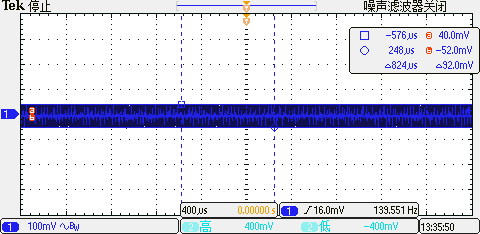
TOP No Load, Negative Rail Ripple: 92 mV
V-F curve:
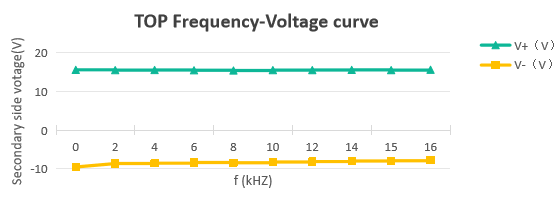
Based on the test data above, it can be concluded that the product demonstrates excellent performance in terms of power supply and load stability. Although Firstack's string inverter driver boards appear structurally simple, we maintain strict control over product performance and quality, ensuring that customers can use our drivers with ease and peace of mind.
As an industry-leading supplier of drive technology, Firstack remains at the forefront of industry trends, continuously pursuing innovation and breakthroughs. Whether through planar transformer technology or multi-channel integration, our solutions align with the development trends of string inverters toward lighter and more highly integrated designs, providing customers with diverse driver solutions for string inverter power modules.
In the future, as photovoltaic technology continues to evolve, IGBT drivers will inevitably advance toward higher performance, greater intelligence, and enhanced reliability. Guided by the philosophy of "Green Driving the Future," Firstack will continue to deepen its expertise in power electronics driving technology, collaborating with industry partners to build a cleaner and more sustainable energy ecosystem.